New Publication: COL4A1-related autosomal recessive encephalopathy in 2 Turkish children
We are happy to have been involved with this paper presenting the neurological phenotypes of 2 Turkish brothers with a novel mutation. Through whole-exome sequencing and analysis using the RD-Connect Genome-Phenome Analysis Platform, we helped to identify a rare case of autosomal recessive inheritance of homozygous missense COL4A1 variants. Widening the clinical spectrum and defining an unusual inheritance pattern of these variants will help clinicians target screening for COL4A1, thus allowing for more appropriate clinical care.
You can read the article on Neurology genetics here.
COL4A1-related autosomal recessive encephalopathy in 2 Turkish children
, , , , , , , , , , , , , ,
Abstract
Objective
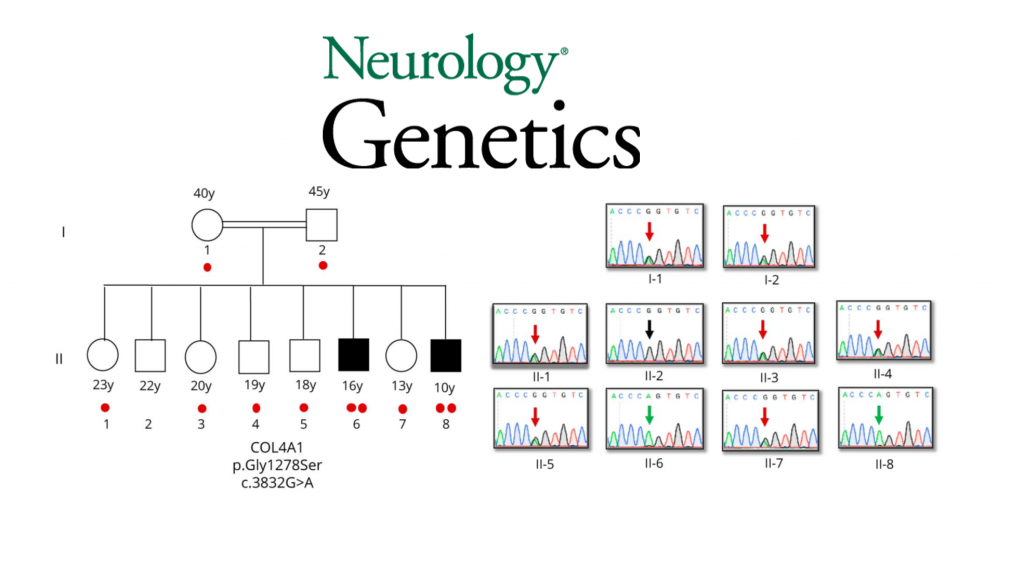
This study presents the neurologic phenotypes of 2 brothers with a novel homozygous COL4A1 mutation that was identified in a large Turkish consanguineous cohort of neurogenetic diseases.
Methods
Whole-exome sequencing and bioinformatic analysis of consanguineous families with children affected by early-onset, neurogenetic disorders was performed using the RD-Connect Genome- Phenome Analysis Platform. We also performed clinical, EEG, and neuroimaging analyses in unaffected siblings and parents.
Results
We have identified a homozygous missense mutation in COL4A1 (p.Gly1278Ser, NM_ 001845.5:c.3832G>T) in 2 siblings affected by small vessel brain disease with periventricular leukoencephalopathy and ocular defects. Presenting symptoms included mild weakness, hemiparetic gait, pyramidal findings, and seizures, whereas their intellectual and behavioral functions were normal. Both parents and 5 of the siblings (3 boys and 2 girls) were heterozygous for the variant. They did not show any clinical or laboratory signs of small vessel disease.
Conclusions
COL4A1 has previously been associated with dominant small vessel disease of the brain and other organs, manifesting with high penetrance in heterozygous mutation carriers. Our findings provide evidence that COL4A1-related encephalopathy can be inherited in an autosomal recessive manner, which is important for counseling, prognosis, and treatment. Genotypephenotype
correlations remain to be established.