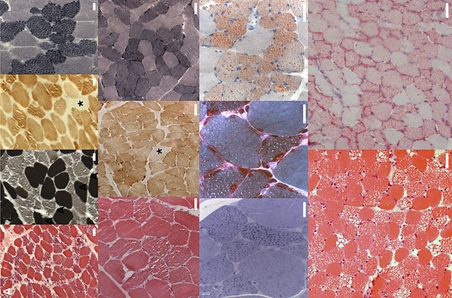
Polavarapu, K, O'Neil, D, Thompson, R, Spendiff, S, Nandeesh, B, Vengalil, S et al.. Partial loss of desmin expression due to a leaky splice site variant in the human DES gene is associated with neuromuscular transmission defects. Neuromuscul Disord. 2024.39 10-18 PMID:38669730
Della Marina, A, Hentschel, A, Czech, A, Schara-Schmidt, U, Preusse, C, Laner, A et al.. Novel Genetic and Biochemical Insights into the Spectrum of NEFL-Associated Phenotypes. J Neuromuscul Dis. 2024.11 (3)625-645 PMID:38578900
Ferreira, T, Polavarapu, K, Olimpio, C, Paramonov, I, Lochmüller, H, Horvath, R et al.. Variants in mitochondrial disease genes are common causes of inherited peripheral neuropathies. J Neurol. 2024.271 (6)3546-3553 PMID:38549004
O'Connor, K, Spendiff, S, Lochmüller, H, Horvath, R. Mitochondrial Mutations Can Alter Neuromuscular Transmission in Congenital Myasthenic Syndrome and Mitochondrial Disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2023.24 (10) PMID:37239850
Roos, A, van der Ven, PFM, Alrohaif, H, Kölbel, H, Heil, L, Della Marina, A et al.. Bi-allelic variants of FILIP1 cause congenital myopathy, dysmorphism and neurological defects. Brain. 2023.146 (10)4200-4216 PMID:37163662
McMacken, G, Whittaker, RG, Wake, R, Lochmuller, H, Horvath, R. Neuromuscular junction involvement in inherited motor neuropathies: genetic heterogeneity and effect of oral salbutamol treatment. J Neurol. 2023.270 (6)3112-3119 PMID:36869887
Van Haute, L, O'Connor, E, Díaz-Maldonado, H, Munro, B, Polavarapu, K, Hock, DH et al.. TEFM variants impair mitochondrial transcription causing childhood-onset neurological disease. Nat Commun. 2023.14 (1)1009 PMID:36823193
Wiessner, M, Roos, A, Munn, CJ, Viswanathan, R, Whyte, T, Cox, D et al.. Mutations in INPP5K, Encoding a Phosphoinositide 5-Phosphatase, Cause Congenital Muscular Dystrophy with Cataracts and Mild Cognitive Impairment. Am J Hum Genet. 2017.100 (3)523-536 PMID:28190456
Herrmann, DN, Horvath, R, Sowden, JE, Gonzalez, M, Sanchez-Mejias, A, Guan, Z et al.. Synaptotagmin 2 mutations cause an autosomal-dominant form of lambert-eaton myasthenic syndrome and nonprogressive motor neuropathy. Am J Hum Genet. 2014.95 (3)332-9 PMID:25192047
Gempel, K, Topaloglu, H, Talim, B, Schneiderat, P, Schoser, BG, Hans, VH et al.. The myopathic form of coenzyme Q10 deficiency is caused by mutations in the electron-transferring-flavoprotein dehydrogenase (ETFDH) gene. Brain. 2007.130 (Pt 8)2037-44 PMID:17412732