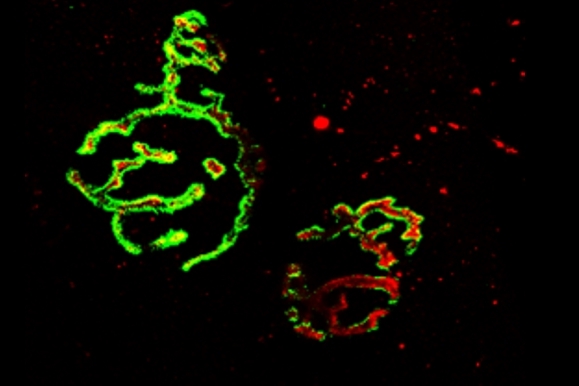
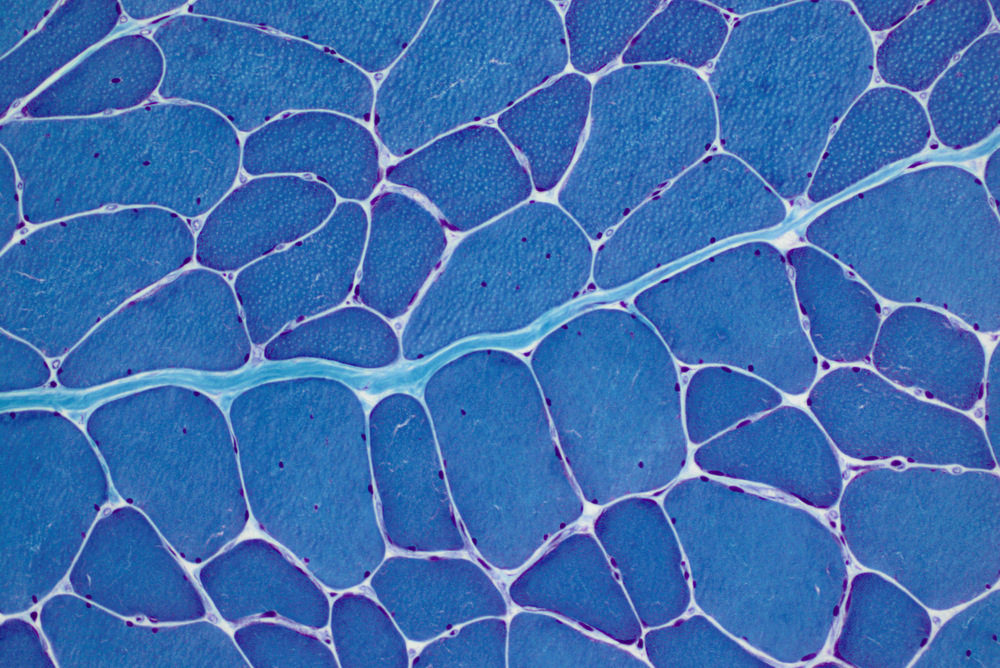
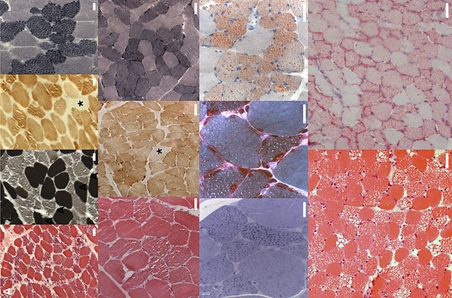
Diseases of interest
Congenital myasthenic syndromes
Congenital myasthenic syndromes (CMS) are rare inherited neuromuscular disorders characterized by fatigable weakness of skeletal muscle owing to compromised function of the neuromuscular junction (NMJ). The first identified mutations were in genes encoding subunits of the acetylcholine receptor, and these remain the most common subtypes of CMS worldwide. With the advent of next-generation sequencing, the number of genetic…
Duchenne muscular dystrophy
Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) is the most common childhood muscular dystrophy and is caused by defects in the DMD gene, which is responsible for making the protein dystrophin. It is an X-linked disease, which means that it affects almost exclusively boys, and is characterized by progressive muscle degeneration and weakness. Affected individuals have proximal muscle…
Spinal muscular atrophy
Spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) affects the motor neurons – the nerve cells responsible for controlling movement of the skeletal muscles. Damage to or complete loss of motor neurons causes muscle wasting or atrophy and weakness. The weakness is usually more severe in the proximal muscles (close to the centre of the body) and usually worsens…
Myotonic dystrophy
Myotonic dystrophy type 1 (DM1) is the most common form of muscular dystrophy in adults. It is a complex, multi-systemic and progressive disorder that leads to severe fatigue, substantial physical functional impairment, and restricted social participation. DM1 is caused by a triplet repeat expansion in the DMPK gene and has autosomal dominant inheritance. Our group is interested in translational research in all areas of this complex disease.
GNE myopathy
GNE myopathy is an autosomal recessive muscle disease caused by mutations in the GNE gene which codes for a protein responsible for the enzymatic activity of UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 2-epimerase and N-acetylmannosamine kinase. Clinical symptoms usually start around the third decade of life with distal muscle weakness, foot drop and difficulty walking. The disease gradually progresses to…
Other inherited neuromuscular conditions
Our research interests often span diseases and encompass a wide range of inherited neuromuscular conditions. Conditions such as DMD and myotonic dystrophy affect hundreds of individuals in Canada, but there are at least another 400 genetically distinct neuromuscular diseases that affect smaller numbers of people. These include mitochondrial myopathies, myofibrillar neuropathies, congenital muscular dystrophies, limb-girdle…