New publication: Advances in the diagnosis of inherited neuromuscular diseases and implications for therapy development
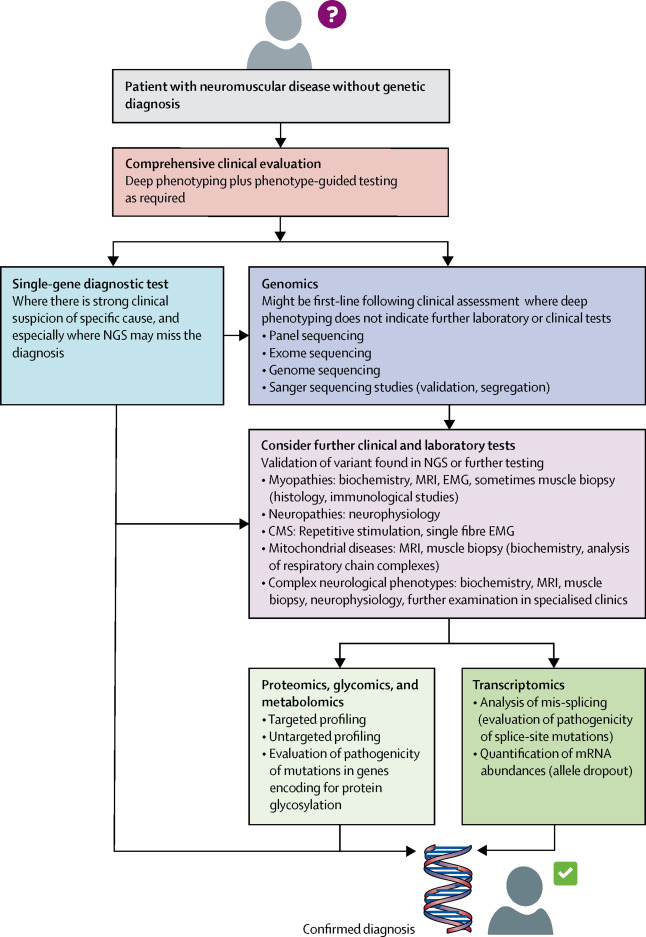
The neuromuscular field has seen rapid advances in recent years thanks to the increased use of next-generation sequencing and additional omics technologies like RNA sequencing and proteomics. Together with colleagues from Ottawa, Germany and the UK, we were delighted to write a new review for the Lancet Neurology in which we show how these new technologies have improved diagnostic rates, increased understanding of disease mechanisms and led to new therapeutic opportunities. We also highlight the continued need for traditional evaluations and the key role that disease experts still play in interpreting the results of the new techniques as leaders of an interdisciplinary approach involving bioinformaticians and data scientists as well as the traditional clinical and biological disciplines. The article is available at the Lancet Neurology website and is temporarily open-access through this dedicated link.
Thompson R, Spendiff S, Roos A, Bourque PR, Warman Chardon J, Kirschner J, Rita Horvath R, Lochmüller H. Advances in the diagnosis of inherited neuromuscular diseases and implications for therapy development. Lancet Neurol. 19(6) 522–532.
DOI: 10.1016/S1474-4422(20)30028-4
Summary
Advances in DNA sequencing technologies have resulted in a near doubling, in under 10 years, of the number of causal genes identified for inherited neuromuscular disorders. However, around half of patients, whether children or adults, do not receive a molecular diagnosis after initial diagnostic workup. Massively parallel technologies targeting RNA, proteins, and metabolites are being increasingly used to diagnose these unsolved cases. The use of these technologies to delineate pathways, biomarkers, and therapeutic targets has led to new approaches entering the drug development pipeline. However, these technologies might give rise to misleading conclusions if used in isolation, and traditional techniques including comprehensive neurological evaluation, histopathology, and biochemistry continue to have a crucial role in diagnostics. For optimal diagnosis, prognosis, and precision medicine, no single ruling technology exists. Instead, an interdisciplinary approach combining novel and traditional neurological techniques with computer-aided analysis and international data sharing is needed to advance the diagnosis and treatment of neuromuscular disorders.