New publication: De-duplicating patient records from three independent data sources reveals the incidence of rare neuromuscular disorders in Germany
Patients with long-term, complex conditions like neuromuscular diseases may receive diagnosis, care and treatment in several different centres, each of which then holds an individual piece of the patient’s complete medical record. These records must be kept confidential to protect the patient’s privacy, but these important privacy restrictions also make it more challenging to link different datasets on the same patient for research purposes or indeed to uncover the precise number of patients affected by a particular condition, since it is not possible to establish whether an individual patient is being counted one or multiple times. A new publication by König et al provides an interesting demonstration of techniques for de-duplicating such patient records using a computational method that involves the creation of a non-identifying hash code for each patient record and thus does not require the patient’s identity to be revealed. This approach was able to reliably identify duplicate records where patients appeared in more than one database and thus to enable a more precise estimation of the incidence of DMD and SMA in Germany.
Read the full (open access) article at the journal website.
De-duplicating patient records from three independent data sources reveals the incidence of rare neuromuscular disorders in Germany.
König K, Pechmann A, Thiele S, Walter MC, Schorling D, Tassoni A, Lochmüller H, Müller-Reible C, Kirschner J.
Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2019 Jun 24;14(1):152.
DOI: 10.1186/s13023-019-1125-2
Abstract
BACKGROUND:

First author Kirsten König
Estimation of incidence in rare diseases is often challenging due to unspecific and incomplete coding and recording systems. Patient- and health care provider-driven data collections are held with different organizations behind firewalls to protect the privacy of patients. They tend to be fragmented, incomplete and their aggregation leads to further inaccuracies, as the duplicated records cannot easily be identified. We here report about a novel approach to evaluate the incidences of Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) and spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) in Germany.
METHODS:
We performed a retrospective epidemiological study collecting data from patients with dystrophinopathies (DMD and Becker muscular dystrophy) and SMA born between 1995 and 2018. We invited all neuromuscular centers, genetic institutes and the patient registries for DMD and SMA in Germany to participate in the data collection. A novel web-based application for data entry was developed converting patient identifying information into a hash code. Duplicate entries were reliably allocated to the distinct patient.
RESULTS:
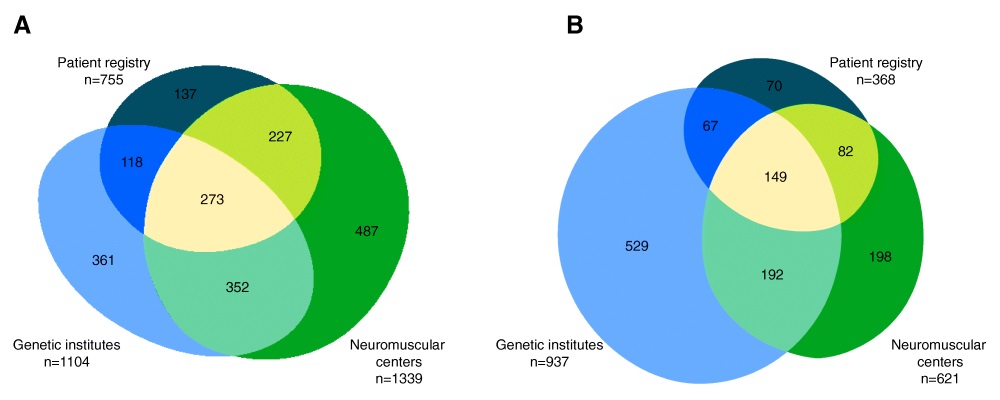
We collected 5409 data entries in our web-based database representing 1955 distinct patients with dystrophinopathies and 1287 patients with SMA. 55.0% of distinct patients were found in one of the 3 data sources only, while 32.0% were found in 2, and 13.0% in all 3 data sources. The highest number of SMA patients was reported by genetic testing laboratories, while for DMD the highest number was reported by the clinical specialist centers. After the removal of duplicate records, the highest yearly incidence for DMD was calculated as 2.57:10,000 in 2001 and the highest incidence for SMA as 1.36:10,000 in 2014.
CONCLUSION:
With our novel approach (compliant with data protection regulations), we were able to identify unique patient records and estimate the incidence of DMD and SMA in Germany combining and de-duplicating data from patient registries, genetic institutes, and clinical care centers. Although we combined three different data sources, an unknown number of patients might not have been reported by any of these sources. Therefore, our results reflect the minimal incidence of these diseases.