New publication: health-related quality of life in myotonic dystrophy type 1 – a systematic review
Our new systematic review by Landfeldt et al on health-related quality of life in myotonic dystrophy type 1 (DM1) is now available online.
DM1 is the most common muscular dystrophy in adults. It is a multisystem disorder that may have a wide range of complications that affect quality of life. In this systematic review we looked at all published articles that reported results on health-related quality of life in adult-onset DM1. Most studies used the SF-36 or the INQoL, which are standard questionnaire-based methods for assessing quality of life. Overall, our review found that the condition does affect quality of life across a wide range of domains, but also that there is substantial variability in the estimates reported between studies. Our results should inform the design and selection of endpoints for future patient trials of new interventions. They also reveal the need for a patient-centred approach to disease management that takes into account the specific domains that each patient needs most support in, and suggest that caregiver burden should also be examined in DM1.
The article is available on the journal website here (open access)
Health-Related Quality of Life in Patients with Adult-Onset Myotonic Dystrophy Type 1: A Systematic Review. Landfeldt, E, Edström, J, Jimenez-Moreno, C, van Engelen, BGM, Kirschner, J, Lochmüller, H et al. Patient. 2019. PMID:30714084
—
Abstract
Background
Adult-onset myotonic dystrophy type 1 (DM1) is a chronic, multisystem disorder that leads to disability and premature death.
Objectives
The objective of our study was to conduct a systematic literature review of the health-related quality of life (HRQoL) of patients with DM1.
Methods
We searched Embase, Web of Science, and PubMed for English language full-text articles reporting results from studies of HRQoL in patients with adult-onset DM1 published between 1 January 2000 and 21 February 2018. We excluded reviews, editorials, and studies reporting results for a sample with fewer than five patients (to allow for meaningful inference).
Results
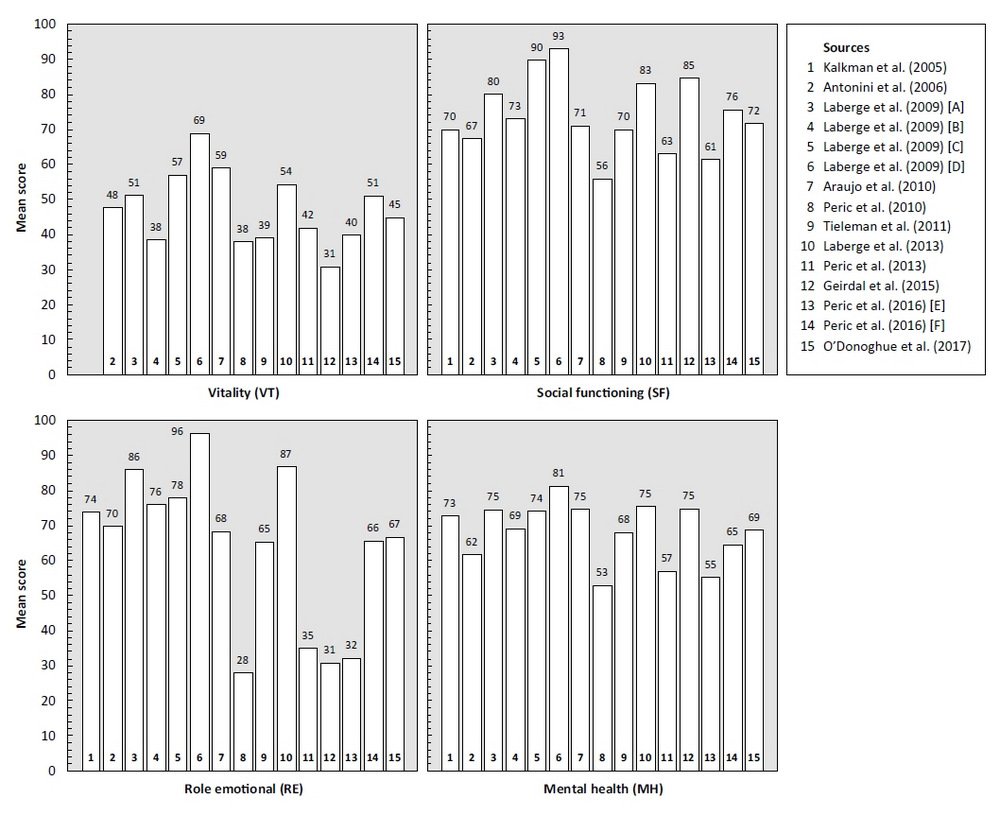
The search identified 266 unique publications. Of these, 231 were excluded following title and abstract screening and 16 after full-text review, leaving 19 articles for data synthesis. We found 15 articles measuring the HRQoL of patients with adult-onset DM1 using the 36-Item Short Form Health Survey (SF-36), six using the Individualized Neuromuscular Quality of Life Questionnaire (INQoL), and one using Cantril’s Ladder. Available evidence shows that patient HRQoL is impaired in DM1, mainly due to compromised physical health, but also reveals that substantial heterogeneity exists in estimates across studies.
Conclusions
HRQoL in adult-onset DM1 has been extensively studied using the SF-36 and the INQoL, but current estimates are inconclusive, and little is known of the impact of the disease as measured using other instruments. Our data synthesis should help characterize the patient burden of DM1 and inform future studies of HRQoL in this indication.