New Publication: MACF1 links Rapsyn to microtubule- and actin-binding proteins to maintain neuromuscular synapses
Determining the mechanism behind a disease causing gene is often very difficult, and yet it remains a key step in the translational pathway towards an effective therapy. That is why we were pleased to collaborate with the Burden Lab on this recent paper identifying the role of MACF1 at the neuromuscular junction (NMJ). Previous research in our group identified patients with congenital myasthenic syndromes with variants in MACF1, yet the pathomechanism remained elusive. Through a combination of biochemical screens, microscopy techniques, and protein assays, it was determined that MACF1 binds Rapsyn, which then binds acetycholine receptors to the microtubule network, hence stabilizing the mature NMJ. Collaborations such as these are vital for rare disease research.
Read the article here.
Abstract
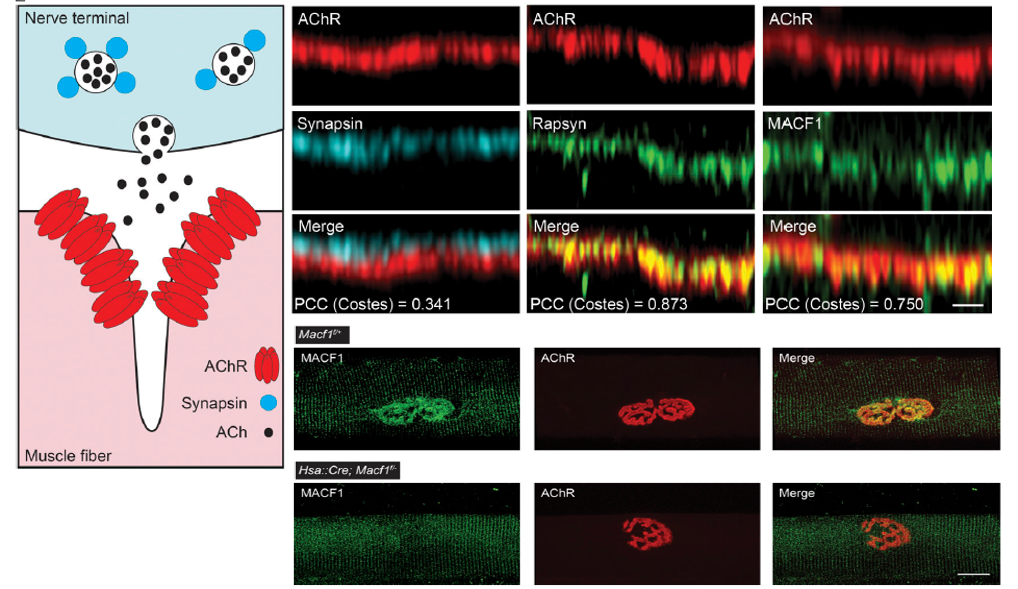
Complex mechanisms are required to form neuromuscular synapses, direct their subsequent maturation, and maintain the synapse throughout life. Transcriptional and post-translational pathways play important roles in synaptic differentiation and direct the accumulation of the neurotransmitter receptors, acetylcholine receptors (AChRs), to the postsynaptic membrane, ensuring for reliable synaptic transmission. Rapsyn, an intracellular peripheral membrane protein that binds AChRs, is essential for synaptic differentiation, but how Rapsyn acts is poorly understood. We screened for proteins that coisolate with AChRs in a Rapsyn-dependent manner and show that microtubule actin cross linking factor 1 (MACF1), a scaffolding protein with binding sites for microtubules (MT) and actin, is concentrated at neuromuscular synapses, where it binds Rapsyn and serves as a synaptic organizer for MT-associated proteins, EB1 and MAP1b, and the actin-associated protein, Vinculin. MACF1 plays an important role in maintaining synaptic differentiation and efficient synaptic transmission in mice, and variants in MACF1 are associated with congenital myasthenia in humans.