New publication: The clinical spectrum of the congenital myasthenic syndrome resulting from COL13A1 mutations
We were pleased to be part of this collaborative effort spearheaded by Pedro M. Rodrıguez Cruz and David Beeson to characterize the mutational and clinical spectrum of congenital myasthenic syndromes (CMS) associated with mutations in COL13A1. This study, which spanned multiple countries, provides a detailed description of the clinical features associated with this particular type of CMS, including how these symptoms change over time. This information not only helps with the recognition and treatment of the condition but also with providing information to patients regarding what to expect in the future.
Find the article on the Brain website here.
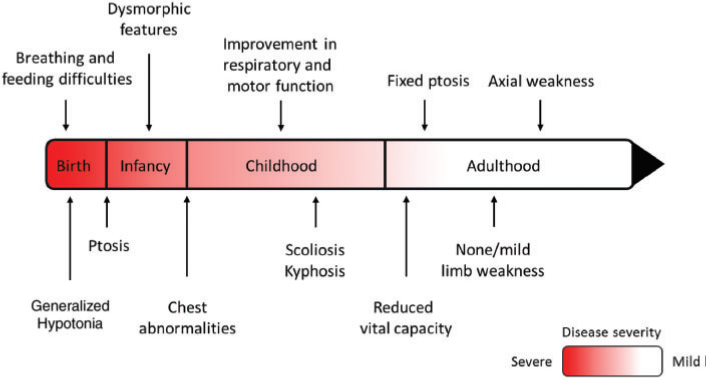
Abstract: Next generation sequencing techniques were recently used to show mutations in COL13A1 cause synaptic basal lamina-associated congenital myasthenic syndrome type 19. Animal studies showed COL13A1, a synaptic extracellular-matrix protein, is involved in the formation and maintenance of the neuromuscular synapse that appears independent of the Agrin-LRP4-MuSK-DOK7 acetylcholine receptor clustering pathway. Here, we report the phenotypic spectrum of 16 patients from 11 kinships harbouring homozygous or heteroallelic mutations in COL13A1. Clinical presentation was mostly at birth with hypotonia and breathing and feeding difficulties often requiring ventilation and artificial feeding. Respiratory crisis related to recurrent apnoeas, sometimes triggered by chest infections, were common early in life but resolved over time. The predominant pattern of muscle weakness included bilateral ptosis (non-fatigable in adulthood), myopathic facies and marked axial weakness, especially of neck flexion, while limb muscles were less involved. Other features included facial dysmorphism, skeletal abnormalities and mild learning difficulties. All patients tested had results consistent with abnormal neuromuscular transmission. Muscle biopsies were within normal limits or showed non-specific changes. Muscle MRI and serum creatine kinase levels were normal. In keeping with COL13A1 mutations affecting both synaptic structure and presynaptic function, treatment with 3,4-diaminopyridine and salbutamol resulted in motor and respiratory function improvement. In non-treated cases, disease severity and muscle strength improved gradually over time and several adults recovered normal muscle strength in the limbs. In summary, patients with COL13A1 mutations present mostly with severe early-onset myasthenic syndrome with feeding and breathing difficulties. Axial weakness is greater than limb weakness. Disease course improves gradually over time, which could be consistent with the less prominent role of COL13A1 once the neuromuscular junction is mature. This report emphasizes the role of collagens at the human muscle endplate and should facilitate the recognition of this disorder, which can benefit from pharmacological treatment.