A new arrival accompanied by a new publication
The Lochmüller lab is pleased to welcome Dr. Emily O’Connor to the group in Ottawa. Emily marked her arrival in the best possible way, with a new publication in the journal Cells, as part of their special issue entitled 150 Years of Motor Endplate: Molecules, Cells, and Relevance of a Model Synapse.
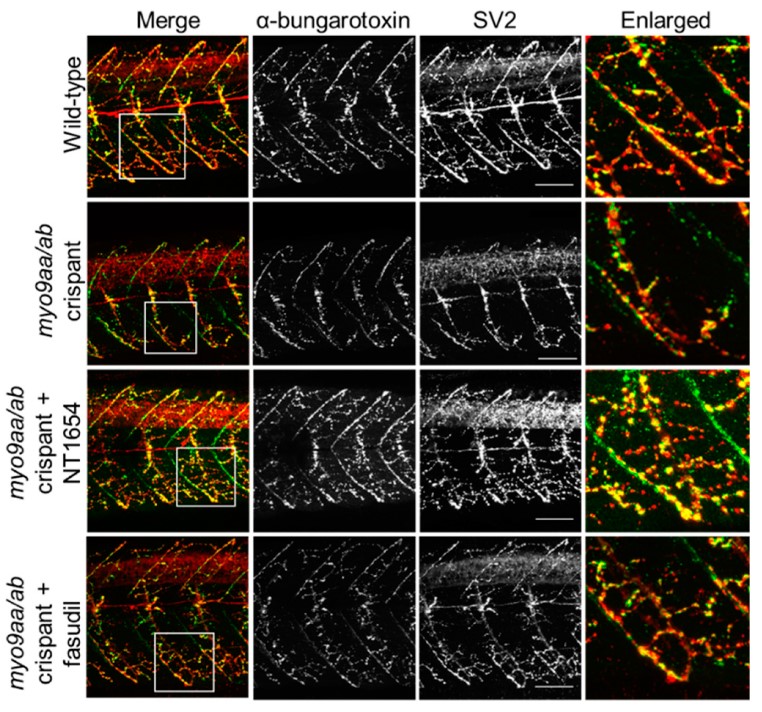
This new study, performed as part of Dr. O’Connor’s PhD work, describes screening of MYO9A-deficient zebrafish for improvements in phenotype after treatment with therapeutic compounds. Impaired function of MYO9A, has been associated with a sub-type of congenital myasthenic syndrome in patients. Zebrafish provide a useful system in which to study loss of neuromuscular junction (NMJ)- proteins due to the large numbers of embryos obtained, their transparency during development, easily accessible NMJs, and ability to perform high throughput drug screening

New lab member Dr. Emily O’Connor
A number of funding organizations contributed to this work including AFM-Téléthon, Kindness for Kids and the Canadian Institutes of Health Research
You can read the full open access article here and learn more about Dr O’Connor’s path to Ottawa here.
Publication Abstract
Congenital myasthenic syndromes (CMS) are a group of rare, inherited disorders characterised by impaired function of the neuromuscular junction (NMJ). This is due to defects in one of the many proteins associated with the NMJ. In three patients with CMS, missense mutations in a gene encoding an unconventional myosin protein, MYO9A, were identified as likely causing their disorder. Preliminary studies revealed a potential involvement of the RhoA/ROCK pathway and of a key NMJ protein, agrin, in the pathophysiology of MYO9A-depletion. In this study, a CRISPR/Cas9 approach was used to generate genetic mutants of MYO9A zebrafish orthologues, myo9aa/ab, to expand and refine the morphological analysis of the NMJ. Injection of NT1654, a synthetic agrin fragment compound, improved NMJ structure and zebrafish movement in the absence of Myo9aa/ab. In addition, treatment of zebrafish with fasudil, a ROCK inhibitor, also provided improvements to the morphology of NMJs in early development, as well as rescuing movement defects, but not to the same extent as NT1654 and not at later time points. Therefore, this study highlights a role for MYO9A at the NMJ, the first unconventional myosin motor protein associated with a neuromuscular disease, and provides a potential mechanism of action of MYO9A-pathophysiology.